The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has issued its Inventory of Mercury Supply, Use, and Trade in the United States 2020 Report, showing that dentistry remains a significant consumer of elemental mercury.
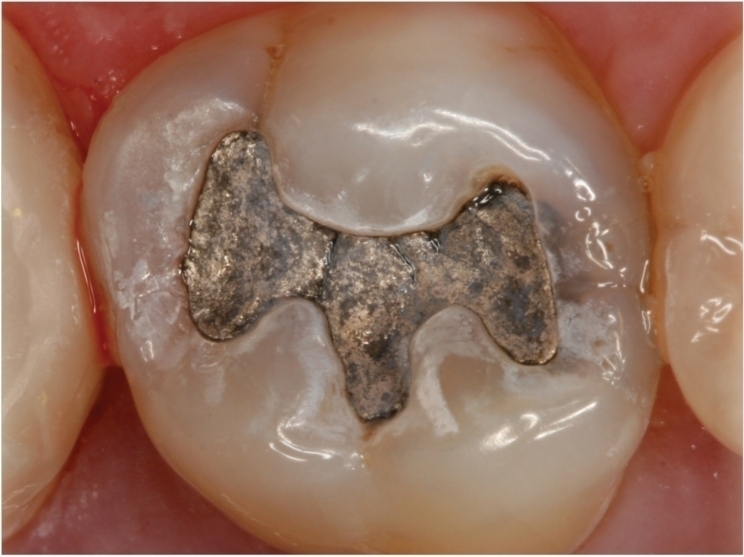
In 2018, 9,287 pounds of elemental mercury was used to make dental amalgam in the United States. That’s 46.8% of the total elemental mercury used. Also, the United States exported 2,624 pounds of elemental mercury in dental amalgam.
Switches, relays, sensors, and valves accounted for 8,915 pounds (44.9%) of elemental mercury used. Lighting, lamps, and bulbs used 1,637 pounds (8.3%). Miscellaneous uses accounted for 1 pound (less than 0.1%).
Mercury is a neurotoxin and heavy metal. About 50% of dental amalgam is elemental mercury by weight. Dental amalgam is a major source of mercury in wastewater, which is why the EPA requires dental practices to recycle any waste amalgam they produce.
The ADA considers dental amalgam to be a safe, affordable, and durable material, noting that it has been used to restore the teeth of 100 million Americans without any systemic adverse effects.
After identifying processes and products that intentionally add mercury as part of its report, the EPA says it will recommend actions to further reduce mercury use including, as appropriate, legal or regulatory actions in accordance with federal statutes.
The EPA also says that it will continue to implement the United States’ obligations under the Minamata Convention on Mercury and participate in the UNEP Global Mercury Partnership, both of which are designed to reduce the adverse effects of the element.
Related Articles
Use of Amalgam Drastically Drops in Fillings in New Zealand
What You Need to Know About the EPA’s Dental Amalgam Rule
Minamata Convention Debates and Rejects Dental Amalgam Ban











